在论文写作和排版过程中,常常会用到算法描述,在LaTex中,算法描述块的排版会用到两个宏包 \usepackage{algorithm} 和 \usepackage{algorithmic}。算法的排版,主要在于控制缩进、粗体、横线等格式,这些都会在这篇博客中进行介绍。
在开始算法排版之前,首先在文档开头加入下面两句,以导入宏包:
\usepackage{algorithm}
\usepackage{algorithmic}
例1
那么,我们首先看一个例子:
\begin{algorithm}
\caption{A}
\label{alg:A}
\begin{algorithmic}
\STATE {set $r(t)=x(t)$}
\REPEAT
\STATE set $h(t)=r(t)$
\REPEAT
\STATE set $h(t)=r(t)$
\UNTIL{B}
\UNTIL{B}
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
在编译之后,显示为:

使用algorithmic包时,关键字全部大写,如果使用的是algorithmicx包,那么关键字首字母大写,后面小写。
例2
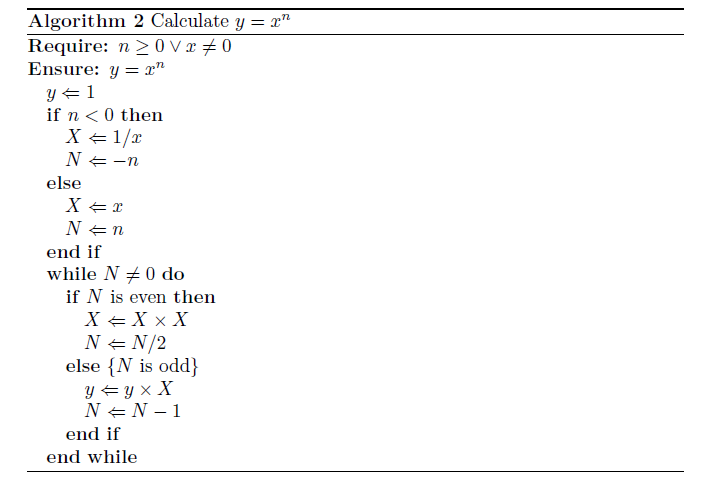
第二个例子更加详细的展示了缩进的控制,可以自己编译一下:
\begin{algorithm}
\caption{Calculate $y = x^n$}
\label{alg1}
\begin{algorithmic}
\REQUIRE $n \geq 0 \vee x \neq 0$
\ENSURE $y = x^n$
\STATE $y \Leftarrow 1$
\IF{$n < 0$}
\STATE $X \Leftarrow 1 / x$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow -n$
\ELSE
\STATE $X \Leftarrow x$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow n$
\ENDIF
\WHILE{$N \neq 0$}
\IF{$N$ is even}
\STATE $X \Leftarrow X \times X$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow N / 2$
\ELSE[$N$ is odd]
\STATE $y \Leftarrow y \times X$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow N - 1$
\ENDIF
\ENDWHILE
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
例3
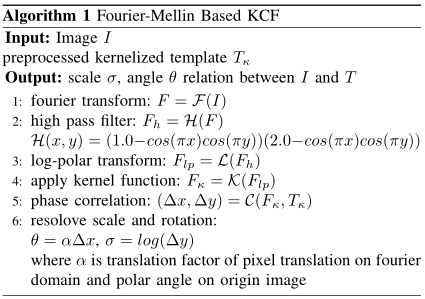
如果需要显示Input和Output:
\begin{algorithm}
\caption{Fourier-Mellin Based KCF}
\label{alg:A}
\hspace*{0.02in}{\bf Input:}
Image $I$\\preprocessed kernelized template $T_\kappa$\\
\hspace*{0.02in}{\bf Output:}
scale $\sigma$, angle $\theta$ relation between $I$ and $T$
\begin{algorithmic}[1]
\STATE {fourier transform: $F=\mathcal{F}(I)$}
\STATE {high pass filter: $F_h=\mathcal{H}(F)$\\$\mathcal{H}(x,y)=(1.0-cos(\pi x)cos(\pi y))(2.0-cos(\pi x)cos(\pi y))$}
\STATE {log-polar transform: $F_{lp}=\mathcal{L}(F_h)$}
\STATE {apply kernel function: $F_\kappa=\mathcal{K}(F_{lp})$}
\STATE {phase correlation: $(\Delta x, \Delta y)=\mathcal{C}(F_\kappa, T_\kappa)$}
\STATE {resolove scale and rotation:\\
$\theta=\alpha \Delta x$, $\sigma=log(\Delta y)$\\
where $\alpha$ is translation factor of pixel translation on fourier domain and polar angle on origin image
}
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
这样,就在开头显示了输入和输出。{algorithmic}[1]表示显示行号,当然,还可以显示竖线,不过要使用额外的宏包,请参考文后博客2链接。
例4
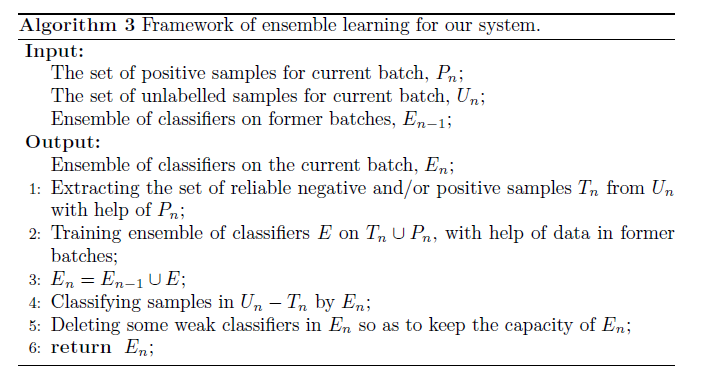
还可以使用\renewcommand 改变现有命令,在导言区加入下列语句
\renewcommand{\algorithmicrequire}{ \textbf{Input:}} %Use Input in the format of Algorithm
\renewcommand{\algorithmicensure}{ \textbf{Output:}} %UseOutput in the format of Algorithm
使得原来软件包中定义的命令\REQUIRE和\ENSURE显示为Input:和Output:
\begin{algorithm}[htb]
\caption{ Framework of ensemble learning for our system.}
\label{alg:Framwork}
\begin{algorithmic}[1] %这个1 表示每一行都显示数字
\REQUIRE ~~\\ %算法的输入参数:Input
The set of positive samples for current batch, $P_n$;\\
The set of unlabelled samples for current batch, $U_n$;\\
Ensemble of classifiers on former batches, $E_{n-1}$;
\ENSURE ~~\\ %算法的输出:Output
Ensemble of classifiers on the current batch, $E_n$;
\STATE Extracting the set of reliable negative and/or positive samples $T_n$ from $U_n$ with help of $P_n$;
\label{ code:fram:extract }%对此行的标记,方便在文中引用算法的某个步骤
\STATE Training ensemble of classifiers $E$ on $T_n \cup P_n$, with help of data in former batches;
\label{code:fram:trainbase}
\STATE $E_n=E_{n-1}\cup E$;
\label{code:fram:add}
\STATE Classifying samples in $U_n-T_n$ by $E_n$;
\label{code:fram:classify}
\STATE Deleting some weak classifiers in $E_n$ so as to keep the capacity of $E_n$;
\label{code:fram:select}
\RETURN $E_n$; %算法的返回值
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
排版结果如下:
例5
最后一个例子:
\begin{algorithm}[h]
\caption{An example for format For \& While Loop in Algorithm}
\begin{algorithmic}[1]
\FOR{each $i \in [1,9]$}
\STATE initialize a tree $T_{i}$ with only a leaf (the root);\
\STATE $T=T \cup T_{i};$\
\ENDFOR
\FORALL {$c$ such that $c \in RecentMBatch(E_{n-1})$}
\label{code:TrainBase:getc}
\STATE $T=T \cup PosSample(c)$;
\label{code:TrainBase:pos}
\ENDFOR
\FOR{$i=1$; $i<n$; $i++$ }
\STATE $//$ Your source here;
\ENDFOR
\FOR{$i=1$ to $n$}
\STATE $//$ Your source here;
\ENDFOR
\STATE $//$ Reusing recent base classifiers.
\label{code:recentStart}
\WHILE {$(|E_n| \leq L_1 )and( D \neq \phi)$}
\STATE Selecting the most recent classifier $c_i$ from $D$;
\STATE $D=D-c_i$;
\STATE $E_n=E_n+c_i$;
\ENDWHILE
\label{code:recentEnd}
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
排版结果为:
